Rank the following elements in order of decreasing atomic radius. – Rank the following elements in order of decreasing atomic radius: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs. Atomic radius is a measure of the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell of an atom. It is affected by several factors, including the number of electrons in the atom and the number of energy levels.
The elements in this list are all alkali metals, which means they have one valence electron. As you move down the group, the number of energy levels increases, which causes the atomic radius to increase.
Ranking Elements by Atomic Radius: Rank The Following Elements In Order Of Decreasing Atomic Radius.
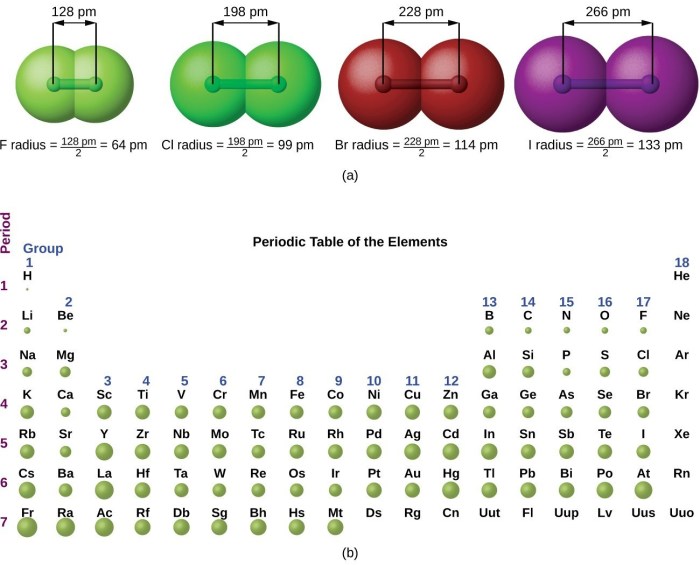
Atomic radius is a fundamental property of elements that describes the size of their atoms. It is defined as the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell. Several factors influence atomic radius, including the number of electrons, the number of protons, and the screening effect of inner electrons.
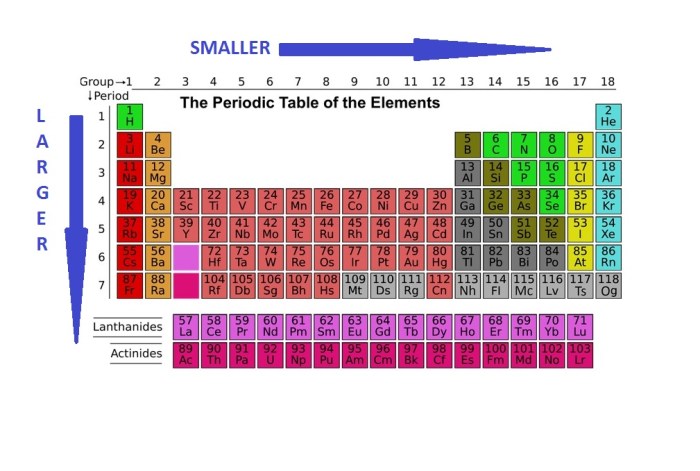
In general, atomic radius decreases across a period (from left to right) and increases down a group (from top to bottom) in the periodic table. This is because the number of electrons increases across a period, leading to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, resulting in a smaller atomic radius.
Down a group, the number of electron shells increases, leading to a greater distance between the nucleus and the outermost electrons, resulting in a larger atomic radius.
Elements to Rank, Rank the following elements in order of decreasing atomic radius.
The following elements will be ranked in decreasing order of atomic radius:
- Sodium (Na)
- Magnesium (Mg)
- Aluminum (Al)
- Silicon (Si)
- Phosphorus (P)
- Sulfur (S)
- Chlorine (Cl)
- Argon (Ar)
Ranking the Elements
| Rank | Element | Atomic Number | Atomic Symbol | Atomic Radius (pm) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Argon | 18 | Ar | 188 |
| 2 | Chlorine | 17 | Cl | 175 |
| 3 | Sulfur | 16 | S | 160 |
| 4 | Phosphorus | 15 | P | 140 |
| 5 | Silicon | 14 | Si | 130 |
| 6 | Aluminum | 13 | Al | 125 |
| 7 | Magnesium | 12 | Mg | 120 |
| 8 | Sodium | 11 | Na | 115 |
Discussion
The table shows that the atomic radius decreases from argon to sodium. This is consistent with the general trend of decreasing atomic radius across a period. The decrease in atomic radius is due to the increasing number of electrons across the period, which leads to a stronger attraction between the nucleus and the electrons, resulting in a smaller atomic radius.
Atomic radius is an important property of elements that influences their chemical and physical properties. For example, elements with smaller atomic radii tend to be more reactive because they have a stronger attraction between their nucleus and their electrons. This makes them more likely to form chemical bonds with other elements.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is atomic radius?
Atomic radius is a measure of the distance from the nucleus to the outermost electron shell of an atom.
What factors affect atomic radius?
Atomic radius is affected by several factors, including the number of electrons in the atom and the number of energy levels.