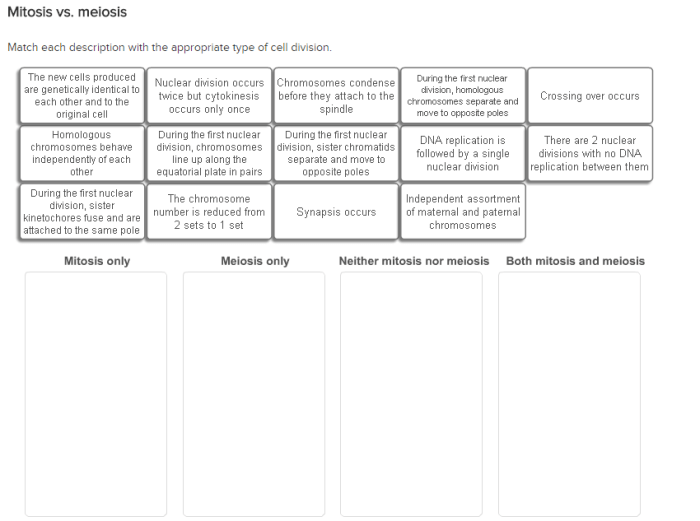
Match each description with the appropriate type of cell division. – Delving into the realm of cell division, this article presents a comprehensive guide to matching cell descriptions with their appropriate division types. From the fundamental concept of cell division to the intricacies of mitosis and meiosis, this exploration unravels the mechanisms that govern cell growth, repair, and reproduction.
As we embark on this journey, we will decipher the distinct characteristics of each cell division type, examining their stages, purposes, and cellular applications. Through a combination of clear explanations, illustrative examples, and comparative analysis, we aim to provide a thorough understanding of this essential biological process.
Cell Division Overview

Cell division is the process by which a cell divides into two or more daughter cells. It is essential for growth, development, and repair of organisms. There are two main types of cell division: mitosis and meiosis.
Types of Cell Division
Mitosis is the process by which a cell divides into two identical daughter cells. It is used for growth and repair of tissues.
Meiosis is the process by which a cell divides into four haploid daughter cells. It is used for the production of gametes (sex cells).
Matching Cell Descriptions to Division Types
| Cell Description | Division Type |
|---|---|
| A cell with 46 chromosomes divides into two cells with 46 chromosomes each | Mitosis |
| A cell with 46 chromosomes divides into four cells with 23 chromosomes each | Meiosis |
| A cell with 23 chromosomes divides into two cells with 23 chromosomes each | Mitosis |
| A cell with 23 chromosomes divides into four cells with 12 chromosomes each | Meiosis |
Mitosis
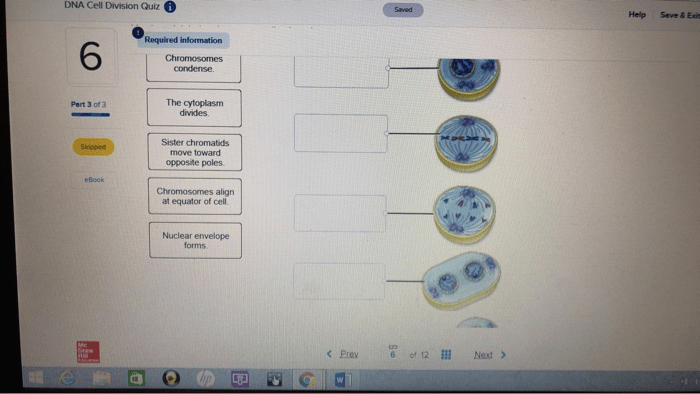
Stages of Mitosis
- Prophase
- Metaphase
- Anaphase
- Telophase
Purpose of Mitosis
Mitosis is used for growth and repair of tissues. It produces two identical daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent cell.
Examples of Cells that Undergo Mitosis
- Skin cells
- Muscle cells
- Bone cells
Meiosis: Match Each Description With The Appropriate Type Of Cell Division.
Stages of Meiosis
- Prophase I
- Metaphase I
- Anaphase I
- Telophase I
- Prophase II
- Metaphase II
- Anaphase II
- Telophase II
Purpose of Meiosis, Match each description with the appropriate type of cell division.
Meiosis is used for the production of gametes (sex cells). It produces four haploid daughter cells that are genetically different from the parent cell.
Examples of Cells that Undergo Meiosis
- Sperm cells
- Egg cells
Comparison of Mitosis and Meiosis
| Characteristic | Mitosis | Meiosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of daughter cells | 2 | 4 |
| Chromosome number in daughter cells | Same as parent cell | Half of parent cell |
| Genetic variation | No | Yes |
| Purpose | Growth and repair | Production of gametes |
Essential FAQs
What is the significance of cell division?
Cell division is essential for growth, repair, and reproduction in all living organisms. It ensures the propagation of genetic material and the creation of new cells to replace old or damaged ones.
How do mitosis and meiosis differ?
Mitosis produces two genetically identical daughter cells, while meiosis produces four genetically diverse daughter cells. Mitosis is used for growth and repair, while meiosis is used for sexual reproduction.
What are some examples of cells that undergo mitosis?
Most somatic cells in the body, such as skin cells, muscle cells, and nerve cells, undergo mitosis.
What are some examples of cells that undergo meiosis?
Gametes, such as sperm and eggs, undergo meiosis.