Double displacement reaction worksheet answers – Delve into the fascinating world of double displacement reactions with our comprehensive worksheet answers. Discover the intricacies of these reactions, their types, and their myriad applications in everyday life and beyond.
Double displacement reactions are a fundamental concept in chemistry, involving the exchange of ions between two ionic compounds. They play a crucial role in various chemical processes, from the formation of precipitates to the neutralization of acids and bases. Our worksheet answers provide a thorough understanding of these reactions, empowering you to confidently tackle any related questions.
Key Concepts: Double Displacement Reactions
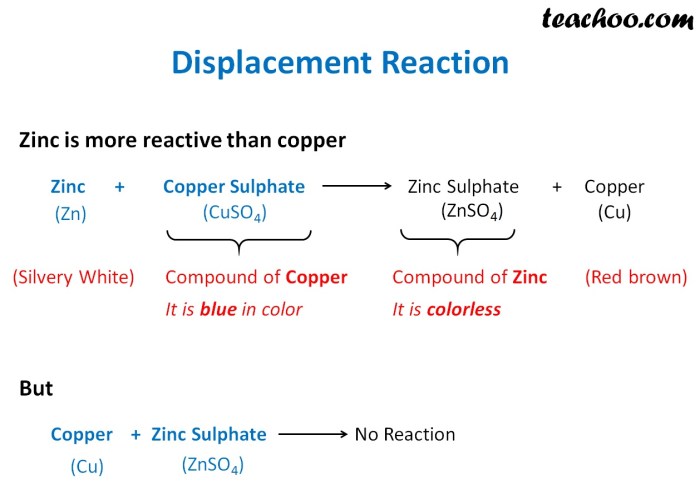
Double displacement reactions are chemical reactions in which the cations and anions of two ionic compounds exchange places to form two new ionic compounds. The general equation for a double displacement reaction is:
AB + CD → AD + CB
For a double displacement reaction to occur, the following conditions must be met:
- The reactants must be in aqueous solution.
- The reactants must be ionic compounds.
- The cations and anions of the reactants must be able to form new ionic compounds that are insoluble in water.
Types of Double Displacement Reactions, Double displacement reaction worksheet answers
Precipitation Reactions
Precipitation reactions are double displacement reactions in which one of the products is an insoluble solid. Precipitation reactions are often used to separate ions from a solution. For example, the reaction of silver nitrate (AgNO 3) and sodium chloride (NaCl) produces silver chloride (AgCl), which is an insoluble solid.
- AgNO 3(aq) + NaCl(aq) → AgCl(s) + NaNO 3(aq)
To predict whether a precipitation reaction will occur, you can use the solubility rules. The solubility rules state that all Group 1 cations (Li +, Na +, K +, Rb +, Cs +), all Group 2 cations (Ca 2+, Sr 2+, Ba 2+), and the ammonium ion (NH 4+) are soluble in water.
All other cations are insoluble in water.
Acid-Base Reactions
Acid-base reactions are double displacement reactions in which one of the reactants is an acid and the other reactant is a base. Acid-base reactions produce a salt and water. For example, the reaction of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium hydroxide (NaOH) produces sodium chloride (NaCl) and water (H 2O).
- HCl(aq) + NaOH(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H 2O(l)
The neutralization reaction that occurs in acid-base reactions is a special type of double displacement reaction. In a neutralization reaction, the acid and base react in stoichiometric amounts to produce a salt and water. The salt is a compound that contains the cation from the base and the anion from the acid.
Gas-Forming Reactions
Gas-forming reactions are double displacement reactions in which one of the products is a gas. Gas-forming reactions are often used to produce gases for industrial purposes. For example, the reaction of hydrochloric acid (HCl) and sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO 3) produces carbon dioxide gas (CO 2).
- HCl(aq) + NaHCO 3(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H 2O(l) + CO 2(g)
To identify the gas produced in a gas-forming reaction, you can use the following rules:
- If one of the reactants is a carbonate (CO 32-) or bicarbonate (HCO 3–) ion, then the gas produced will be carbon dioxide (CO 2).
- If one of the reactants is a sulfide (S 2-) ion, then the gas produced will be hydrogen sulfide (H 2S).
- If one of the reactants is a nitrate (NO 3–) ion, then the gas produced will be nitrogen dioxide (NO 2).
Applications of Double Displacement Reactions
Double displacement reactions have a wide variety of applications in everyday life, industry, and analytical chemistry.
- Everyday life:Double displacement reactions are used in baking, cleaning, and many other everyday activities. For example, the reaction of baking soda (NaHCO 3) and vinegar (CH 3COOH) produces carbon dioxide gas, which makes baked goods rise. The reaction of soap (a salt) and hard water (which contains calcium and magnesium ions) produces insoluble calcium and magnesium salts, which remove the hardness from the water.
- Industry:Double displacement reactions are used in a variety of industrial processes, such as the manufacture of paper, glass, and fertilizers. For example, the reaction of calcium carbonate (CaCO 3) and sulfuric acid (H 2SO 4) produces calcium sulfate (CaSO 4), which is used to make paper.
The reaction of sodium chloride (NaCl) and ammonia (NH 3) produces sodium hydroxide (NaOH), which is used to make glass. The reaction of ammonia (NH 3) and nitric acid (HNO 3) produces ammonium nitrate (NH 4NO 3), which is used as a fertilizer.
- Analytical chemistry:Double displacement reactions are used in analytical chemistry to identify and quantify ions in solution. For example, the reaction of silver nitrate (AgNO 3) with an unknown solution can be used to identify the presence of chloride ions (Cl –). If chloride ions are present, a white precipitate of silver chloride (AgCl) will form.
Helpful Answers: Double Displacement Reaction Worksheet Answers
What are the necessary conditions for a double displacement reaction to occur?
For a double displacement reaction to occur, the reactants must be in aqueous solution and the ions present must be able to form a precipitate, gas, or water.
How can you predict whether a precipitation reaction will occur?
To predict whether a precipitation reaction will occur, you can use the solubility rules. If the cation of one reactant and the anion of the other reactant are both insoluble, then a precipitate will form.
What is the neutralization reaction that occurs in acid-base reactions?
In acid-base reactions, the hydrogen ions from the acid react with the hydroxide ions from the base to form water.