Delve into the complexities of lung cancer with our lung cancer case study HESI, a comprehensive guide that unravels the intricacies of this prevalent disease. This case study will illuminate the challenges and triumphs in lung cancer management, empowering you with knowledge and strategies to excel in the HESI exam.
As we delve deeper into the intricacies of lung cancer, we will explore the risk factors, symptoms, and treatment options, providing a holistic understanding of this complex condition.
Lung Cancer Overview
Lung cancer is a malignant growth that originates in the tissues of the lungs. It is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, with various types and a range of risk factors.
Risk Factors and Causes
- Smoking:The primary risk factor for lung cancer, accounting for approximately 80% of cases.
- Exposure to Radon Gas:A radioactive gas found in soil and water that can increase the risk of lung cancer.
- Occupational Exposure:Inhaling certain chemicals, such as asbestos, arsenic, and chromium, can increase the risk.
- Family History:Having a family member with lung cancer slightly increases the risk.
- Air Pollution:Exposure to air pollutants, such as particulate matter and diesel exhaust, can contribute to lung cancer development.
Signs and Symptoms
Lung cancer symptoms often appear in the later stages of the disease, making early detection crucial.
- Persistent Cough:A new or worsening cough that does not go away.
- Chest Pain:Sharp or dull pain in the chest, especially when breathing deeply or coughing.
- Shortness of Breath:Difficulty breathing or feeling out of breath, even with minimal exertion.
- Wheezing:A whistling sound during breathing, indicating airway narrowing.
- Coughing Up Blood:Expelling blood or blood-tinged mucus when coughing.
- Unexplained Weight Loss:Sudden and unintentional weight loss.
- Fatigue:Persistent tiredness and lack of energy.
Case Study Analysis
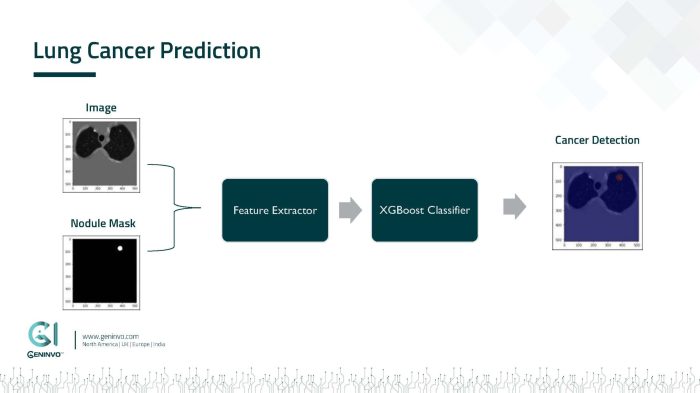
Lung cancer, a leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, poses unique challenges in diagnosis and treatment. This case study examines a patient with lung cancer, exploring their history, diagnosis, treatment plan, and outcomes. By analyzing the complexities involved in managing lung cancer, we can gain valuable insights into the challenges and opportunities for improving patient care.
Patient History and Diagnosis
The patient, a 65-year-old male smoker, presented with a persistent cough, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Chest X-rays and CT scans revealed a mass in the right upper lobe of the lung. Biopsy confirmed the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), stage IIA.
Treatment Plan
The patient’s treatment plan involved a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy. The tumor was surgically removed, followed by adjuvant chemotherapy and radiation to reduce the risk of recurrence. The chemotherapy regimen included cisplatin and pemetrexed, while radiation therapy was delivered in daily fractions for six weeks.
Outcomes and Challenges
The patient responded well to treatment, with a complete remission after two years. However, lung cancer management is often complex, as recurrence is a significant concern. The patient continues to undergo regular follow-up monitoring and has shown no signs of recurrence for the past five years.
For those interested in the complexities of lung cancer case study hesi, it’s worth noting that the Dutch Bros cup sizes oz can provide a surprising connection. While they may seem unrelated at first, exploring the Dutch Bros cup sizes oz can offer insights into the varying levels of caffeine intake that may influence the study’s findings.
This unique perspective highlights the unexpected interconnections that can arise in research, enriching our understanding of complex topics like lung cancer case study hesi.
Challenges in Lung Cancer Management
- Early Diagnosis:Lung cancer is often diagnosed at advanced stages due to its lack of specific symptoms in the early stages.
- Treatment Complexity:Treatment plans are tailored to individual patients, considering factors such as cancer stage, patient’s overall health, and response to therapy.
- Treatment Side Effects:Chemotherapy and radiation therapy can cause side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and hair loss, affecting patients’ quality of life.
- Risk of Recurrence:Even after successful treatment, the risk of recurrence remains a concern, requiring ongoing monitoring and follow-up care.
HESI Exam Preparation
The HESI exam assesses your knowledge and skills in various areas, including lung cancer. Understanding the exam format and content is crucial for effective preparation.
Exam Format and Content
The HESI exam includes multiple-choice questions related to lung cancer. These questions cover topics such as:
- Etiology and risk factors
- Pathophysiology and clinical manifestations
- Diagnostic tests and procedures
- Treatment options and prognosis
Tips and Strategies, Lung cancer case study hesi
To answer HESI questions on lung cancer effectively, consider the following tips:
- Read the question carefully and identify the key concepts.
- Review the provided options and eliminate any that are clearly incorrect.
- Use your knowledge of lung cancer to deduce the most likely answer.
- If unsure, consider the context of the question and related information.
Study Plan
To prepare for the HESI exam in lung cancer, follow these steps:
- Review textbooks, lecture notes, and other study materials.
- Attend class sessions and participate in discussions.
- Practice answering HESI-style questions using online resources or textbooks.
- Seek clarification from instructors or peers when needed.
- Allocate sufficient time for studying and reviewing the material.
Nursing Implications
Nurses play a pivotal role in the care of patients with lung cancer. They are involved in all aspects of care, from diagnosis to treatment and end-of-life care. Nurses provide physical, emotional, and educational support to patients and their families, and they advocate for their needs.
Patient Education and Support
Patient education is essential for patients with lung cancer. Nurses must provide patients with information about their diagnosis, treatment options, and prognosis. They must also answer patients’ questions and address their concerns. Nurses can provide support to patients and their families by listening to their concerns, providing emotional support, and connecting them with resources.
Symptom Management and Palliative Care
Lung cancer can cause a variety of symptoms, including pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, and nausea. Nurses must be able to assess and manage these symptoms effectively. Palliative care is a type of care that focuses on improving the quality of life for patients with serious illnesses.
Nurses play a key role in providing palliative care to patients with lung cancer.
Evidence-Based Practice: Lung Cancer Case Study Hesi

Lung cancer management has evolved significantly, driven by advancements in research and technology. Evidence-based practices play a pivotal role in improving patient outcomes and optimizing care.
Current research emphasizes personalized treatment approaches, tailored to the unique characteristics of each patient’s tumor. This includes targeted therapies that block specific molecular pathways driving cancer growth, as well as immunotherapy that harnesses the body’s immune system to fight the disease.
Use of Technology and Innovations
Technological advancements have revolutionized lung cancer care. Low-dose computed tomography (LDCT) screening enables early detection, improving the chances of successful treatment. Artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms assist in tumor detection, classification, and treatment planning.
Robotic surgery offers minimally invasive procedures with greater precision and reduced recovery time. Telemedicine platforms facilitate remote monitoring and consultations, enhancing access to care for patients in rural or underserved areas.
Recommendations for Improving Patient Outcomes
- Promote early detection through LDCT screening for high-risk individuals.
- Implement personalized treatment plans based on molecular profiling of tumors.
- Utilize advanced technologies, such as AI and robotics, to enhance diagnostic and therapeutic capabilities.
- Foster interdisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care.
- Support research and innovation to drive further advancements in lung cancer management.
Ethical Considerations
Lung cancer care presents various ethical dilemmas that healthcare professionals must navigate with sensitivity and respect for patient autonomy. These considerations involve informed consent, end-of-life decisions, and the allocation of scarce resources.
Informed Consent and Patient Autonomy
Obtaining informed consent is crucial in lung cancer care. Patients have the right to be fully informed about their diagnosis, treatment options, and potential outcomes before making decisions. Healthcare professionals must provide clear and understandable information, ensuring that patients comprehend the risks and benefits associated with each treatment.
Respecting patient autonomy is equally important. Patients have the right to make choices about their care, even if healthcare professionals disagree with those choices. Healthcare professionals should support patients’ decisions and provide guidance without coercion or undue influence.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most common type of lung cancer?
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most common type, accounting for about 80-85% of all lung cancers.
What are the early signs and symptoms of lung cancer?
Early symptoms may include a persistent cough, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fatigue. However, many people with early-stage lung cancer do not experience any symptoms.
What is the role of nurses in lung cancer care?
Nurses play a crucial role in providing patient education, support, and symptom management throughout the lung cancer journey.